1. What Is Anti-Aging Medicine?
Anti-aging medicine is the branch of medicine which aims to reduce the chance of developing aging-related arteriosclerosis and other aging-related diseases, including cancer, by intervening in the biological process of aging, and thereby contributing to the extension of a healthy life span.
As shown by the Government’s recent establishment of the late-stage medical care system for elderly, health maintenance of the elderly has become a national issue in Japan. Anti-aging medicine has come to play an increasingly important role not only from the viewpoint of individual happiness, but also with regard to the economic efficiency of society.
Japanese health policy has traditionally focused on the treatment of disease after its onset under a universal healthcare system. This approach will almost certainly lead to massive increases in medical expenses, likely resulting in the collapse of the national health insurance system.
The tide of healthcare is set to change, with greater importance attached to preventive medicine. With its focus on aging, anti-aging medicine plays a central role in preventive medicine, and logically the ultimate role.
2. Definition of Anti-Aging Medicine
Anti-Aging Medicine is a theoretical and practical science whichaimstohelp people to enjoy health and longevity.
Enjoying health means more than prolonging life span. What matters is the quality of life.
Hence the emphasis is placed on the quality of life span.
People can enjoy health and longevity even if they have a disease. In this context, even if an age-related pathological condition develops, the key is the maintenance of holistic health – a sense of comfort, both physically and mentally – and well-balanced state.
Theoretical and practical science that aims to allow people to enjoy health and longevity
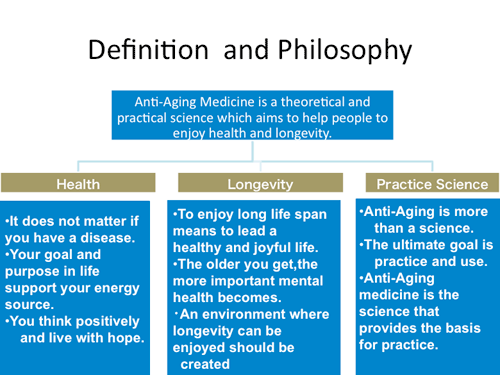
Health
・It does not matter if you have a disease.
・Your goal and purpose in life support your energy source.
・You think positively and live with hope.
Longevity
・To enjoy long life span means to lead a healthy and joyful life.
・The older you get, the more important mental health becomes.
・An environment where longevity can be enjoyed should be created (nation and people).
Practical science
・Anti-Aging is more than a science.
・The ultimate goal is practice and use.
・Anti-Aging medicine is the science that provides the basis for practice.
3. Why Focus on Anti-Aging Medicine Now?
Public interest in coping with aging and life management through consultation with and support from physicians and healthcare professionals is growing.
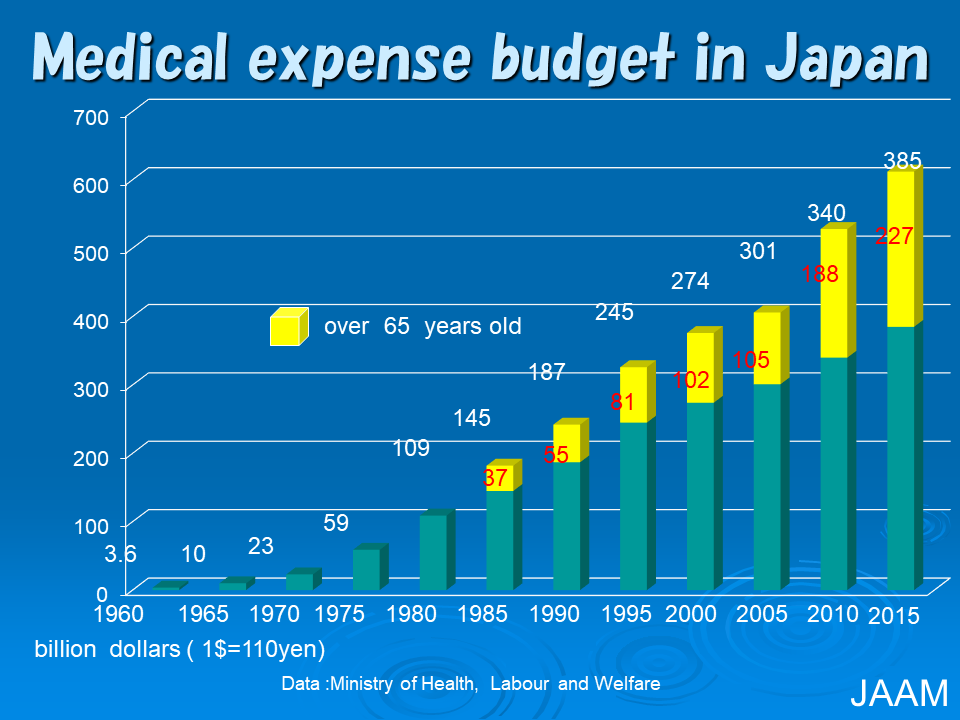 With the aging of the population and decrease in birth rate, the burden of medical expenditures covered by the public healthcare insurance system is about to reach a critical limit. If many of the elderly population stay healthy, however, this burden could be of its present level.
With the aging of the population and decrease in birth rate, the burden of medical expenditures covered by the public healthcare insurance system is about to reach a critical limit. If many of the elderly population stay healthy, however, this burden could be of its present level.
The elderly are defined as those aged 65 years or older. If the healthy elderly population grows, they may be able to continue to work as taxpayers. Anti-aging medicine can contribute to making this scenario come true.
4. Basics of Anti-Aging Medicine
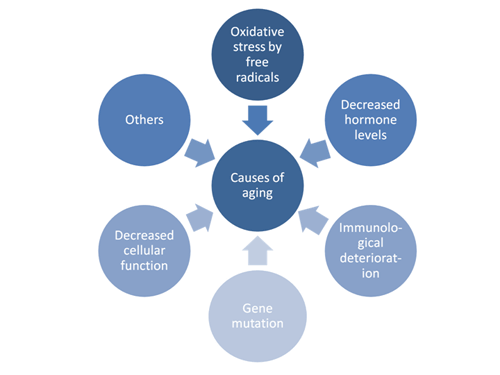
The basic element of anti-aging medicine is to elucidate the aging mechanism. Many of the mechanisms of the biological process of aging, however, remain unknown.
Meanwhile, a number of causal factors of aging have been identified by basic research in different fields, including gene mutation, decreased cellular function, free radical oxidization, immunological deterioration, and decreased hormone level. JAAM strives to keep up with the latest findings and insights gained in these fields to cope with diverse causal factors of aging through anti-aging medicine.
Causes of aging
Oxidative stress by free radicals
Decreased hormone levels
Immunological deterioration
Gene mutation
Decreased cellular function
Others
5. Clinical Anti-Aging Medicine
In addition to the traditional comprehensive medical checkup, age-related physical changes as well as signs and symptoms of aging can be identified by examining blood vessels, hormone levels, functions of sensory organs, balance between active oxygen and antioxidant potential, and others. These examinations enable early detection and treatment as well as lifestyle guidance to prevent aging-related diseases. It is crucial to identify the signs of aging and take appropriate measures as early as possible. The basic elements of clinical anti-aging medicine consist of measures to improve the lifestyle of patients: dietary advice, including guidance on the use of nutritional supplements, exercise programs, and stress control.
When selecting a therapy, the risks and benefits of each therapy should be examined with the utmost importance placed on safety.
Some medical institutions may use hormone replacement therapy. Others may use chelation therapy, the evidence for which is, while not abundant, considered to demonstrate efficacy in removing heavy metals from the body.
Approaches taken in different areas
Areas covered by anti-aging medicine (from specialized areas to covering the whole body)
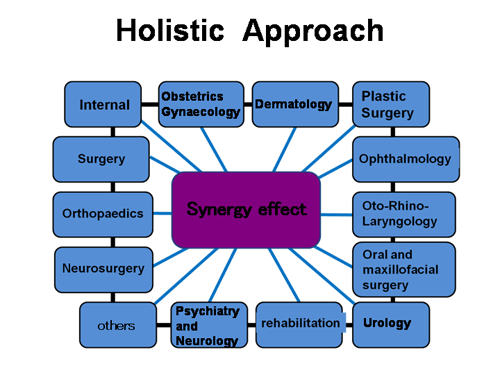
Internal medicine
Metabolism
Cardiovascular
Digestive tract
Endocrine
Respiratory
Neurology
Cerebrovascular disorder
Alzheimer’s disease
Stress
Orthopedics
Muscle weakness
Osteoporosis
Osteoarthritis
Ophthalmology
Presbyopia
Cataract
Age-related macular degeneration
Obstetrics and gynecology
Menopausal disorders
Late childbearing
Hormonal issues
Urology
Sexual dysfunction
Male climacteric disorder
Prostate disorder/hormonal issues
Dermatology
Photoaging
Senile dermatitis
6. What Is Anti-Aging Medicine/Diagnosis?
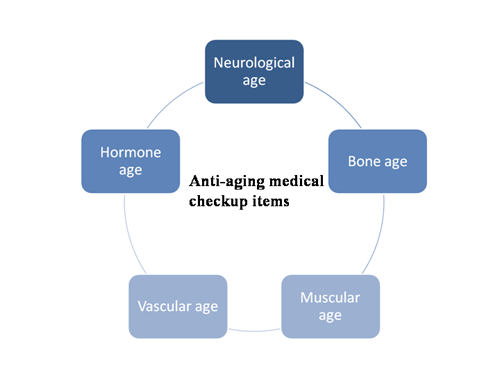
Anti-aging medical checkup
In addition to the traditional comprehensive medical checkup, age-related physical changes as well as signs and symptoms of aging can be identified by examining blood vessels, hormone levels, functions of sensory organs, balance between active oxygen and antioxidant potential, etc. These examinations enable early detection and treatment as well as lifestyle guidance to prevent aging-related diseases. Early identification of and action against the signs of aging is crucial. The basic elements of the anti-aging medical checkup consist of measures to improve the lifestyle of patients: dietary instruction, including guidance on the use of nutritional supplements, exercise programs, and stress control.
Examination for disease prevention and early treatment
・Biomarkers are measured and their results and age index calculated.
・Metabolic syndrome, which is associated with multiple lifestyle disease risk factors, is identified at an early stage for prevention and early treatment.
・Aging and deterioration of quality of life (QOL; level of mental, physical, social, cultural, and intellectual satisfaction in daily life) are identified at an early stage for prevention and early treatment.
Guidance and treatment based on anti-aging diagnosis
・Based on the examination results, anti-aging medical specialists provide guidance on diet, nutritional supplements, and exercise to improve lifestyle, thereby preventing aging and age-related diseases and prolonging a healthy life span.

Daily guidanc
・Nutritional therapy
・Exercise therapy
・Mental therapy
Supplement therapy
・Physician selection criteria
Drug therapy
・Hormone replacement therapy
・Immune enhancement therapy
・Antioxidant therapy
Special therapy
・Plastic surgical/dermatological treatment
・Alternative medicine
Anti-aging medical checkup items
Neurological age
Bone age
Muscular age
Vascular age
Hormonal age





